Marketing
Radiocarbon dating false - Pula
Geologic Dating Methods: Are They Always Accurate?

Dating Site: Radiocarbon dating false
These two measures of time will only be the same if all of the assumptions which go into the conventional radiocarbon dating technique are valid. Other similar theories include that candle smoke rich in carbon dioxide and the volatile carbon molecules produced during the two fires may have altered the carbon content of the cloth, rendering carbon-dating unreliable as a dating tool. The improvements to these curves are based on new data gathered from tree rings, , , plant , , and. For a set of samples forming a sequence with a known separation in time, these samples form a subset of the calibration curve.
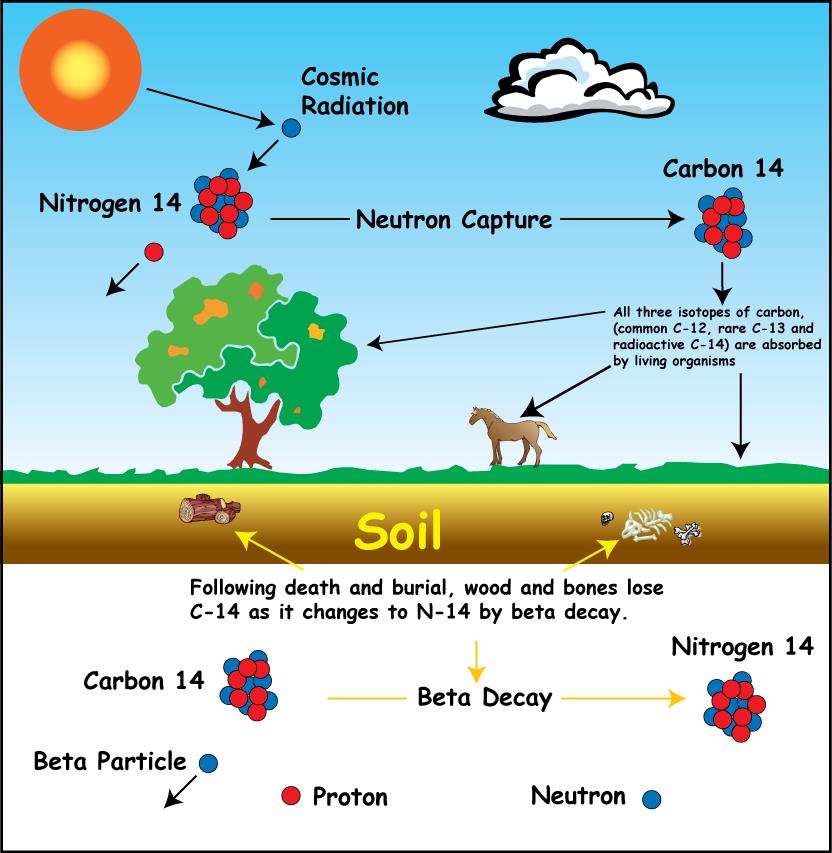
Mollusks The shells of living mollusks have been dated using the carbon 14 method, only to find that the method gave it a date as having been dead for 23,000 years! It invalidates the sample and thus the conclusion of the tests. Assertion 1: Radiocarbon dates are based on the assumption that the atmospheric 14C to 12C ratio has been constant in the past.

Carbon-14 dating - The date of the eruption is known to be around 1800-1801. The procedures for taking the samples and treating the results were discussed by representatives of the three chosen laboratories at a meeting at the British Museum in January 1988 and their recommendations 4 were subsequently approved by the Archbishop of Turin.

Radioactive Dating, Accurate or Not?
Since trees can have a lifespan of hundreds of years, its date of death might not even be relatively close to the date the archaeologists are looking for. Were enough serious mistakes made to call the results into question? If so, the restoration would have had to be done with such incredible virtuosity as to render it microscopically indistinguishable from the real thing. The development of radiocarbon dating has had a profound impact on. This effect is known as isotopic fractionation. Rogers also noted that fibers in the Raes material contained less lignin than the rest of the shroud. To determine the age of a sample whose activity has been measured by beta counting, the ratio of its activity to the activity of the standard must be found. Our research demonstrates that ring-shaped structures with false cavities are common features of individuals belonging to Adansonia digitata that achieve large dimensions and old ages. The other common technology used for measuring 14 C activity is liquid scintillation counting, which was invented in 1950, but which had to wait until the early 1960s, when efficient methods of benzene synthesis were developed, to become competitive with gas counting; after 1970 liquid counters became the more common technology choice for newly constructed dating laboratories. Kouznetsov's results could not be replicated, and no actual experiments have been able to validate this theory, so far. These organisms contain about 1.
[The hookup fau address|Speed dating jku|Oq significa dating]
Post je objavljen 16.01.2019. u 17:52 sati.