Marketing
Hepatitis A, B, C - Datiranje za seks
Expert Answers: What Are the Differences Between Hepatitis A, B, and C?

Click here: Hepatitis A, B, C
R: La hepatitis es una inflamación del hígado. The largest mRNA, which is longer than the viral genome , is used to make the new copies of the genome and to make the core protein and the viral. Su infecciosidad disminuye rápidamente una vez que la ictericia se hace evidente.
Treatment for autoimmune hepatitis involves very effective medicines that suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. A growing body of evidence shows that antiviral therapy initiated in the third trimester significantly reduces transmission to the neonate. The New England Journal of Medicine, 370, 1973. However, this drops to 30% for younger children, and only 5% of newborns that acquire the infection from their mother at birth will clear the infection.
10 Signs and Symptoms of Hepatitis C - Infection is rare in the United States but rates are high in the developing world Africa, Asia, Central America, Middle East. The source of these chemicals can be external, such as medications or alcohol, or internal, such as ammonia or bilirubin.
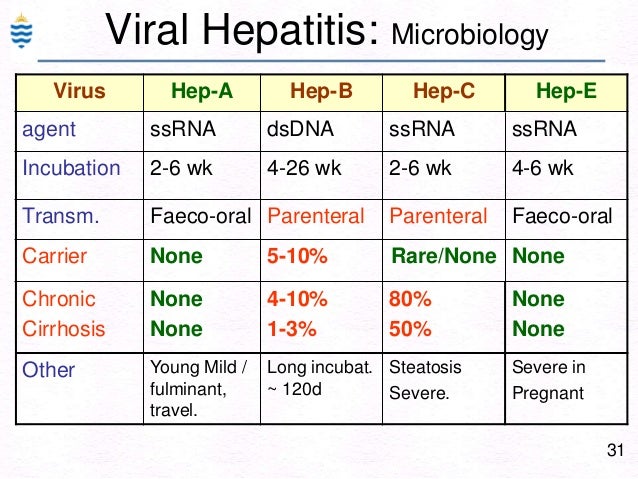
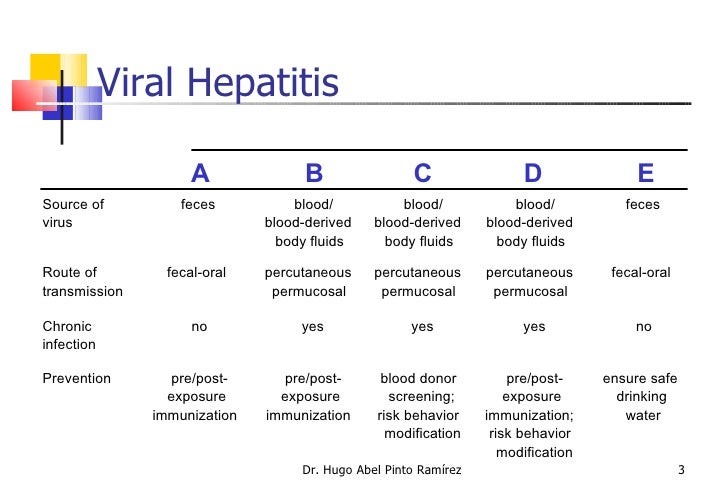
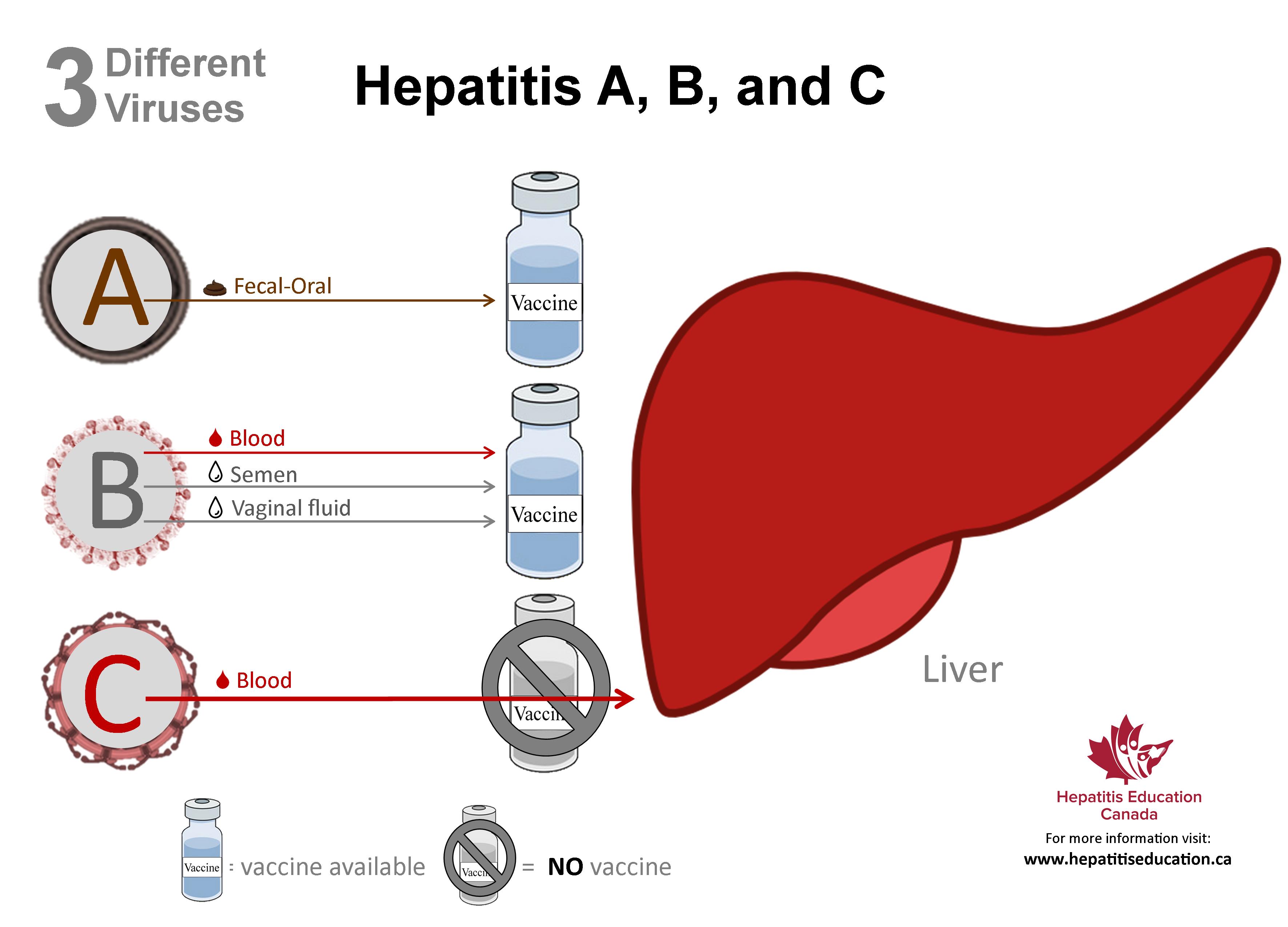
Hepatitis refers to an inflammatory condition of the liver. These include autoimmune hepatitis and hepatitis that occurs as a secondary result of medications, drugs, toxins, and alcohol. Your is located in the right upper area of your abdomen. Treatment options vary depending on which type of hepatitis you have. You can prevent some forms of hepatitis through immunizations and lifestyle precautions. Viral infections of the liver that are classified as hepatitis include hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. A different virus is responsible for each type of virally transmitted hepatitis. Hepatitis A is always an acute, short-term disease, while hepatitis B, C, and D are most likely to become ongoing and chronic. Hepatitis E is usually acute but can be particularly dangerous in pregnant women. Hepatitis A is caused by an infection with the hepatitis A virus HAV. This type of hepatitis is most commonly transmitted by consuming food or water contaminated by feces from a person infected with hepatitis A. Hepatitis B is transmitted through contact with infectious body fluids, such as blood, vaginal secretions, or semen, containing the hepatitis B virus HBV. Injection drug use, having sex with an infected partner, or sharing razors with an infected person increase your risk of getting hepatitis B. Hepatitis C comes from the hepatitis C virus HCV. Hepatitis C is transmitted through direct contact with infected body fluids, typically through injection drug use and sexual contact. HCV is among the most common bloodborne viral infections in the United States. Hepatitis D Also called delta hepatitis, is a serious liver disease caused by the hepatitis D virus HDV. HDV is contracted through direct contact with infected blood. Hepatitis D is a rare form of hepatitis that only occurs in conjunction with hepatitis B infection. Hepatitis E is a waterborne disease caused by the hepatitis E virus HEV. Hepatitis E is mainly found in areas with poor sanitation and typically results from ingesting fecal matter that contaminates the water supply. This disease is uncommon in the United States. However, cases of hepatitis E have been reported in the Middle East, Asia, Central America, and Africa, according to the. Alcohol and other toxins Excessive alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This is sometimes referred to as. The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to and , a thickening and scarring of the liver. Other toxic causes of hepatitis include overuse or overdose of medications and exposure to poisons. Autoimmune system response In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as a harmful object and begins to attack it. It causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. If you have infectious forms of hepatitis that are chronic, like hepatitis B and C, you may not have symptoms in the beginning. Symptoms may not occur until the damage affects liver function. Signs and symptoms of acute hepatitis appear quickly. History and physical exam To diagnose hepatitis, first your doctor will take your history to determine any risk factors you may have for infectious or noninfectious hepatitis. Your doctor may also feel to see if your liver is enlarged. If your skin or eyes are yellow, your doctor will note this during the exam. Liver function tests use blood samples to determine how efficiently your liver works. High liver enzyme levels may indicate that your liver is stressed, damaged, or not functioning properly. Other blood tests If your liver function tests are abnormal, your doctor will likely order other blood tests to detect the source of the problem. These tests can check for the viruses that cause hepatitis. They can also be used to check for antibodies that are common in conditions like autoimmune hepatitis. Ultrasound An uses ultrasound waves to create an image of the organs within your abdomen. This test allows your doctor to take a close at your liver and nearby organs. This can be a useful test in determining the cause of your abnormal liver function. Liver biopsy A is an invasive procedure that involves your doctor taking a sample of tissue from your liver. Typically, an ultrasound is used to guide your doctor when taking the biopsy sample. This test allows your doctor to determine how infection or inflammation has affected your liver. It can also be used to sample any areas in your liver that appear abnormal. Treatment options are determined by which type of hepatitis you have and whether the infection is acute or chronic. Bed rest may be recommended if symptoms cause a great deal of discomfort. The hepatitis A vaccine is available to prevent this infection. Most children begin vaccination between ages 12 and 18 months. Vaccination for hepatitis A is also available for adults and can be combined with the hepatitis B vaccine. Chronic hepatitis B is treated with antiviral medications. This form of treatment can be costly because it must be continued for several months or years. Treatment for chronic hepatitis B also requires regular medical evaluations and monitoring to determine if the virus is responding to treatment. Hepatitis B can be prevented with vaccination. The recommends hepatitis B vaccinations for all newborns. The series of three vaccines is typically completed over the first six months of childhood. The vaccine is also recommended for all healthcare and medical personnel. Hepatitis C Antiviral medications are used to treat both acute and chronic forms of hepatitis C. People who develop chronic hepatitis C are typically treated with a combination of antiviral drug therapies. They may also need further testing to determine the best form of treatment. People who develop cirrhosis scarring of the liver or liver disease as a result of chronic hepatitis C may be candidates for a. Currently, there is no vaccination for hepatitis C. Hepatitis D No antiviral medications exist for the treatment of hepatitis D at this time. According to a , a drug called alpha interferon can be used to treat hepatitis D, but it only shows improvement in about 25 to 30 percent of people. Hepatitis D can be prevented by getting the vaccination for hepatitis B, as infection with hepatitis B is necessary for hepatitis D to develop. Hepatitis E Currently, no specific medical therapies are available to treat hepatitis E. Because the infection is often acute, it typically resolves on its own. People with this type of infection are often advised to get adequate rest, drink plenty of fluids, get enough nutrients, and avoid alcohol. However, pregnant women who develop this infection require close monitoring and care. Autoimmune hepatitis Corticosteroids, like prednisone or budesonide, are extremely important in the early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. Azothioprine , a drug that suppresses the immune system, is often included in treatment. It can be used with or without steroids. Other immune suppressing drugs like mycophenolate CellCept , tacrolimus Prograf and cyclosporine Neoral can also be used as alternatives to azathioprine for treatment. Hygiene Practicing good hygiene is one key way to avoid contracting hepatitis A and E. Practicing safe sex by using and can help decrease the risk of infection. You can find many options available for purchase. Vaccines The use of vaccines is an important key to preventing hepatitis. Experts are currently developing vaccines against hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis B or C can often lead to more serious health problems. Certain supplements and medications can also affect liver function. If you have chronic hepatitis B or C, check with your doctor before taking any new medications. Healthline and our partners may receive a portion of revenues if you make a purchase using a link above.
Hepatitis A B C '2015
Chronic infection is a long-term condition, lasting more than six months. The condition usually resolves if the underlying cause is treated successfully. This is to protect your liver from additional damage. Se multiplica en el hígado pero puede estar presente fuera de él. El hígado es el órgano más grande dentro de su cuerpo. The treatment reduces viral replication in the liver, thereby reducing the the amount of virus particles as measured in the blood. Es una infección aguda que no cronifica. Una serie de exámenes de sangre llamados se realizan cuando hay sospecha de hepatitis. Annals of Internal Medicine.
[Usamljena srca dijaspora|Tajni sex|Ponude za brak -- Mali Oglasi # Goglasi.com]
Post je objavljen 21.12.2018. u 21:35 sati.