|

| < |
lipanj, 2019 |
> |
| P |
U |
S |
Č |
P |
S |
N |
| |
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
| 3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
| 10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
| 17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
| 24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
Srpanj 2020 (1)
Lipanj 2020 (1)
Svibanj 2020 (1)
Travanj 2020 (1)
Ožujak 2020 (1)
Veljača 2020 (1)
Siječanj 2020 (1)
Prosinac 2019 (2)
Srpanj 2019 (1)
Lipanj 2019 (2)
Svibanj 2019 (1)
Travanj 2019 (1)
Veljača 2019 (1)
Prosinac 2018 (2)
Studeni 2018 (1)
Rujan 2018 (4)
Srpanj 2018 (1)
Ožujak 2018 (3)
Veljača 2018 (1)
Prosinac 2017 (3)
Studeni 2017 (2)
Links
VIDEOS FROM THE MEETING IN CROATIA
|
|
24.06.2019., ponedjeljak
ABOUT MATHEMATICS ... discreetly Activity for June 2019.
Activitiy description:
7th graders took part in the Cryptology Workshop, where they introduced with the fact what cryptology is and how cryptography is one of its branches and how they evolved through history.
Furthermore, they had the opportunity to work with skytal - stick by which the Spartans encrypted their messages from the 5th century BC. Cr. Skital was a wooden stick around which a parchment ribbon was wrapped around, and the message was vertical written. After typing the message, the ribbon would be folded away and there would be mixed signs that only the one with a stick of the same thickness could read. The students got sticks of different thickness and paper that wrapped around the stick and wrote their messages.
They noticed that this simple encryption method was very effective because they could not decipher other messages without a stick of the same thickness.
Polibi square
After that, they decrypted the messages by using the Polibi square. Polybias was a Greek (and Roman) historian who studied and wrote during the 2nd century BC. Cr. He took over and perfected the idea of ��Greek mathematicians by using a simple mathematical method of using the numbers and the coordinate system to send encrypted (secret) messages. The polybium square is essentially a square of 25 fields (5 rows of 5 columns). Each field has one letter, besides the field that contains the letters I and J. Each row and column is numbered 1 to 5 so each letter is assigned a pair of numbers. By using the Polibi square, the students have decrypted the names of partner countries.
After that, they got a little more contemporary version of the Polibi square, where instead of the letters they got smilies and this version of the Polibi square is adapted for mobile phones. These activities should be deciphered by "I Love Mathematics".
The last activity is related to Gaj Julije Cezar. He is the creator of Caesar's code whose aim is to replace a certain letter with the letter that is three places further from it in the alphabet (A ’ D, B ’ E, etc.).
In order to make it easier for students to use Caesar's code with an arbitrary shift, instead of summing up, students can use a circle ("wheel") made of cardboard with all alphabetic letters printed in the row. Let the circle ("wheel") consist of two circular portions. It is necessary to fix the outer part so that the inner part can rotate in the circle. So we get all 25 possible combinations of open and encrypted alphabet. The students cut their circles and joined them so that the inner circle could rotate around the outside, which is necessary. There was a word written on the board that did not make any sense and the key was given to students (C = F). The students set up their "Caesar wheels" and deciphered the default term.
Activity aim:
The popularization of mathematics with an emphasis on the development of creativity, curiosity and imagination. The security of the cryptosystem lies precisely in our inability to quickly and efficiently solve the appropriate problem in the area of algebra, number theory or combinatorics. Interesting encryption methods and in particular the detection of methods for breaking the encryption system will enable students to experience the power and beauty of math. Also, to connect the teaching of Math and History.
Contemporary methods of work:
Learning and teaching conducted by discovery and conversation
Learning outcomes:
Getting to know cryptology and seeing how cryptography is a part of cryptology and how a major role in mathematics it has with all its domains. The popularization of mathematics and the connection of mathematics teaching to history teaching.
Activity results:
The students have adopted the basics of cryptography: basic algorithm (Alice -Bob -Eve), encryption (encryption), decryption and key. In history examples, they coded or decoded the default codes and observed the development of cryptography as well as its growing importance (from military, intelligence and diplomatic services to telecommunications and banking). Simply said, cryptology has become our daily life.
Additionally
The workshop was created and accomplished by History teacher Martina Grundler Hrala in in cooperation with Math teacher Anita Jukić and English teacher Azra Benković.
The activity is accompanied by making a short film in English which will be released on a
transnational meeting in Croatia in July 2019.
In purpose of making this kind of a film, the activity is translated in English and leading actors are students who present their knowledge through the activity (student Lorena Filić). For documenting the activity we are going to use multimedia equipment, photo camera, camera, internet, Youtube channel and Adobe Premiere Pro program (student Tvrtko Kolarić).
|
23.06.2019., nedjelja
BETWEEN US … ORGANISMS Activity for April/May 2019.
WORKSHOP 1
INTRODUCTION
Talking to students, explain the purpose of the activity. Think, based on our own experience, how many times we have been in a situation to intervene in the relationship between the prey and the predator trying to disable the predator in his intentions. Of course, we would save the prey, victim and conclude that we did a good deed. But is that so? Ask the question: What would happen if, for example, people would often release frogs from the copperhead's jaws or sparrow from the hawk's claws so that predators always kill each other? The students will conclude that this would lead to the appearance of a large number of frogs and sparrows and to the destruction of the copperheads and hawks. The consequence of such order of organisms in nature would disturb the number of other living beings that feed frogs and sparrows and ultimately lead to their extinction. In the end, food would disappear, and frogs and sparrows would disappear. And that would be the end of it. Explain the students how this kind of event is called an ecological catastrophe.
In this way, the students should become aware that this relationship between organisms implies interdependence in the diet creates the only possibility of preserving life on our planet. That is why this relationship is the most important. 7th graders will learn this school year about biolinbiology teaching systematics by studying their anatomy, physiology, ecology and evolution. Using the acquired knowledge, within the project "Mathematics-the queen of science", students will explore the nutritional relations between the parks of the Papuk Nature Park with a special emphasis on the Ivanjski rovaš type. It's group activity, workshop entitled: "I EAT, YOU EAT, HE EATS - RELATIONSHIP THAT KEEPS LIFE ON EARTH" (subtitle: "The nutritional realtion between Ivanjski rovaš and other organisms of the Park Papuk Nature Park"). After the presentation of a rare, strictly legally protected and the smallest lizard in Croatia, noticed 2008 only in the Papuk Nature Park and at several locations in Ilok, students will be divided into three groups.

Group 1: The production of food chains that include PP Papuk organisms grouped according to the diet in the producers and consumers of I, II, III and IV order and featuring Ivanjski rovaš as consumer II order.
Group 2: Production of nutrition grid (intertwined feeding chains - one member appears in multiple chains) based on analysis of the first group's work.
Group 3: Production of nutritional pyramids (number among members of individual nutrition groups) based on established relationships between organisms in food chains and nutritional grid after analysing works of 1st and 2nd groups.
Activity aim
To stimulate students' interest in science by researching nutritional habits of organisms, to develop students logical thinking and inference by placing individual organisms into appropriate food groups, to encourage environmental awareness among students to act
responsible and by respecting natural laws without harmful interference, provide the maintance of natural balance in the area where they live.
Motivation for activity comes from the fact that someone always eats something in nature and that is completely normal. By acquiring this natural legacy, it enables the circulation of matter and the flow of energy through the living being, which is the foundation of the entire life in the Earth. So, nutrition relations among organisms most clearly represent the dynamics of life that excludes any monotony.
Contemporary methods of work: collaborative learning, research work using ICT, dialogue method, writing methods, reading methods with understanding of teaching assignments, skillful drawing methods and color expression.
Learning Outcomes: Students will differentiate eating habits of particular species and their role in the food chain, assamble and explain nutrition chains, link feeding chains to nutritional grid and shape nutritional pyramid, monitor the abundance of organisms of specific habitat.
Activity Outcomes: Based on the established nutritional relations, the students conclude on the importance of conservation of all species, so that each of them contributes to a stable natural balance and the maintenance of the life we ��know it. Consequently, the students will conclude that they are involved in this process in their daily lives by taking the place of the highest order consumer - collectors, plowmen and hunters who have no natural enemies. Therefore, man carries the greatest responsibility.
The activity is created and accomplished by students and Biology teacher Brankica Safin.


WORKSHOP 2
Within another workshop called "Between Us ... organisms", students are examining examples of relations between living organisms.
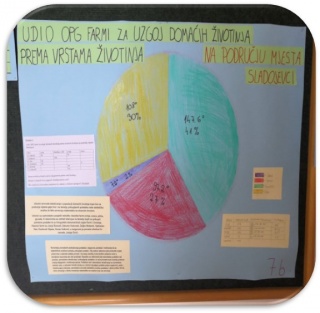
They are conducting a research on the population of domestic animals that live in the same area as they do and based on collected data ,
they are doing statistical analysis and that way they link math to real life.
The students visited,on their own, several owners of pig farms, sheep, chickens, cattle. The owners held interviews based on which they collected the necessary information and photographed the farm and the animals. The owners of the farms are Josip Šomođi, Zdravko Vukovski, Željko Bobanić, Vjekoslav Hes, Goran Vuković, Dunković Dijana, and interviews were conducted by a student of the 6th grade, Josipa Dorić.
     
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The students also contacted an expert associate of Papuk Nature Park biologist Marko Doboš, who assisted them in collecting data on the populations of wildlife in the Papuk Nature Park. The students conducted a statistical analysis of the number of reptiles found at the research areas: copperhead, minnow, green lizard, Natrix tessellata, Anguis fragilis, Coronella austriaca, Viviparous lizard , European viper, wall lizard, sand lizard, Ablepharus kitaibelii. Research areas are : Jankovac (JA), Zvečevo (ZV), Svinjarevac (SV), Djedovica (DJ), Fosilno nalazište (FN), Bistra (BI), Vetovo - ribnjaci (VR), Kutjevo - potok (KP) Dubočanka - brook (DU), Brzoja (BR), Orahovac lake (OJ), Slatinski Drenovac (SD), Lake Voćin (VJ), Sekulinci potok (SP), Dubok potok (DP). The analysis is based on the published scientific work of T. Bogdanović, F. Barišić, "Papuk Nature Park Reptiles", Hyla Association.
Based on researches and conversations, there is also a motivation for statistical analysis to show the collected data. The aim of this workshop is to awaken the students' awareness of the importance of nature conservation and environmental conservation, and that society depends entirely on the Earth's resources if it wants to survive. The result of this activity is self-contained practical work by students, self-research and data gathering, and the development of students' creativity when drawing diagrams and editing billboards. Practical work and independent research are modern methods of work, and learning outcomes are achieved: students gather information through conversations, queries and research on the Internet, perform statistical analysis of data and their presentation on their own. In this way, they understand the close correlation of mathematics with the world around us.The workshop was created and accomplished by Mathematics teachers Anita Jukić and Denis Vujanović.
Additionally
The activity is accompanied by making a short film in English which will be released on a transnational meeting in Croatia in July 201. In purpose of making this kind of a film, the activity is translated in English and leading actors are students who present their knowledge through the activity. For documenting the activity we are going to use multimedia equipment, photo camera, camera, internet, Youtube channel and Adobe Premiere Pro program (student Tvrtko Kolarić).
Translating, English teacher Azra Benković.
|
|