Increasing System Bitrate or Using WDM Technology?
ponedjeljak , 31.10.2016.Introduction
With the fast development of the optical network, the demand for wider bandwidth and faster data transmission rates over farther distances are increasing day by day, which makes more and more fiber cables need to be installed when the optical network is designed. However, once the available fiber infrastructure is exhausted and can’t meet the increasing communication need any more, laying more fibers would become an impracticable or uneconomical method. Thereby, new capacity for the network needs to be created. In order to solve this, experts try to fall back on two new methods to expand the capacity of our network: increasing system bitrate to multiplex more signals and using WDM (wavelength division multiplexing) technology.
Comparison Between Increasing System Bitrate and Using WDM Technology
It is well known that both increasing system bitrate to multiplex more signals and using WDM technology can expand the capacity of our network. But the fact is that WDM technology is more commonly used for expanding the capacity of our network. What makes WDM technology so popular in optical network? What’s the advantage of WDM technology? The following will introduce the two methods of expanding the capacity of our network and seek the differences of the two methods.
Increasing System Bitrate
Nowadays, most of our systems have already worked in 2.5 GB network. If we want to increase our system bitrate to multiplex more signals for expanding capacity, we should upgrade our system to 10 GB network. However, the upgrading process requires changing out all the electronics in our network which should be an expensive project. Taking the high upgrade cost into consideration, it is not recommended to expand capacity by increasing system bitrate to multiplex more signals.
Using WDM Technology
In contrast to upgrading our system, using WDM technology to expand the capacity of our network should be a quite advisable, cost-effective way that doesn’t require more fiber cables or changing out the electronics in our network. WDM technology takes great advantage of the enormous bandwidth of the optical fiber and makes bidirectional communications via one strand of fiber possible. To be brief, WDM technology creates virtual fibers to transmit data, which is the optimal method to expand capacity in optic network at present. As WDM technology is developed fast and tended to be mature, it is strongly advised to use this technology for promoting the network with high-volume data transmission over one single optical fiber.
More Things About WDM Technology You Should Know
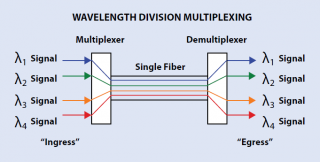
The word of WDM stands for wavelength-division multiplexing. From its name, it is easy to know that the technology is using different wavelengths of light from a laser or a LED to multiplex two or more optical carrier signals over a single optical fiber. In its working process, without using additional fibers, optical carrier signals with different wavelengths are combined at the ingress, then transmitted together through the single optical fiber, and finally separated into individual signals with differing wavelengths at the express again as shown in the following figure.
At present, there are two types of WDM technology, CWDM (coarse wavelength division multiplexing) and DWDM (dense wavelength division multiplexing), both of which are indispensable and popular technologies to expand capacity on the fiber links. To some extent, WDM technology strongly multiplies the capacity of the network that plays an important role in meeting the increasing requirement of modern network.
Conclusion
The WDM revolution has already occurred with unexpected swiftness, which is more popular and commonly used for expanding the capacity than increasing system bitrate in today’s network. Although WDM technology is lack of a long history, the maturity of the technology have been realized WDM systems tailored specifically to the metropolitan area, providing high bandwidth and high capacity at a relatively low cost.
komentiraj (0) * ispiši * #
Introduction of Some Commonly Used MPO/MTP Products
petak , 28.10.2016.Introduction
With the popularity of cloud computing and big data, the data throughput continually increases, which makes 40/100G Ethernet network more commonplace and now become a prevalent trend for data-center. In order to keep pace with the rapidly developing network, there are a series of MPO/MTP products designed for the reliable and quick operations in high-density data centers, such as, MTP/MPO trunk cable, MTP/MPO harness cable and MPO/MTP cassette. Have you ever wondered what do MPO/MTP stand for? What are the functions of these MPO/MTP products? In this article, it will give the explanation for MPO/MTP and some commonly used MPO/MTP products for your reference.
MPO/MTP Technology Overview
The word MPO is also referred to as “Multiple-Fiber Push-On/Pull-off”, while MTP is a upgrade version of the former MPO, with better optical and mechanical performance. As a high-density, high-performance solution for data centers, MPO/MTP technology is deployed for multi-fiber applications by pulling just one single cable with multiple fibers. Through this technology, you can replace 12 or 24 LC connectors with only one MPO/MTP connector. Generally, MPO/MTP technology is widely used for 40/100G Ethernet network as well as fast installation of enterprise data centers nowadays.
MPO/MTP Patch Cable
MPO/MTP patch cable is composed of MPO/MTP cable and MPO/MTP connectors, which is commonly used when 40G or 100G active transceivers (e.g., QSFP+ and QSFP28 transceivers) are employed with MTP/MPO interface. For its special internal structure of multi-fiber, MPO/MTP patch cable has a great improvement in performance, for example, less space, scalability, thereby significant space and cost savings are provided to user. As for MTP/MPO connector, it has many fiber optic channels to transmit signals, which becomes the up-and-coming standard optical interface for 40/100G Ethernet network.
Generally, there are two commonly used MPO/MTP patch cables, MTP/MPO trunk cable and MTP/MPO harness cable, which occupy the most part of high density multi-fiber cables market.
MTP/MPO Trunk Cable
MTP/MPO trunk cable is available with 12, 24, 48 and 72 fibers. For instance, a 72-fiber trunk cable can be terminated with 6 MPO/MTP connectors. It usually serves as a permanent link connecting MPO/MTP modules to each other, which is a great solution to reduce the time cost with easy installation and eliminate termination errors. Another advantage is to take up less space, which is very convenient to use. In short, it plays an important role in the data centers with high density requirement and may be the best choice for permanent connection.
MTP/MPO Harness Cable
MTP/MPO harness cable is designed for the transition from multi-fiber cables to single fiber cables or between the duplex connectors, which provides a reliable, cost-effective cabling system for migrating from legacy 10G to higher speed 40G/100G Ethernet. With the property of flexible connections, MTP/MPO harness cable is indispensable for high-density data centers.
MPO/MTP Cassette
MPO cassette modules are usually fitted with 12 or 24 fibers, with LC, SC or E2000 adapters on the front side and MPO/MTP adapters at the rear. As a high density module, it can distribute the fibers brought by a trunk cable to a duplex cable that serves the transition from ribbon cables terminated with MPO/MTP connector to more common LC or SC interface used on the transceiver terminal equipment.
Conclusion
Compared with traditional fiber products, there are many improvements in MPO/MTP Products, such as, faster and easier installation, lower cost and higher density with less space. There is no doubt that more and more MPO/MTP products will be developed to meet the increasingly high demand of data centers, which will eventually flood the high-density data center.
komentiraj (0) * ispiši * #
Simplex vs. Duplex Fiber Jumpers
ponedjeljak , 24.10.2016.Introduction
Instead of copper jumper, fiber jumper plays an important role in telecommunication infrastructures, with a great improvement in the properties of repeatability, confidentiality, transmission speed and transmission capacity to realize the data transmission with low loss. For its largely use, there are a wide range of fiber jumpers available on the market developed for different aims, such as, single mode fiber jumpers, duplex fiber jumpers, ST to LC Fiber Jumper, etc. Different fiber jumpers vary from the color of fiber jumpers to their applications, which can be classified by different standard. In this paper, it will mainly introduce the differences between simplex and duplex fiber jumpers that are classified according to different cable quantities.
Simplex VS. Duplex Fiber Jumpers
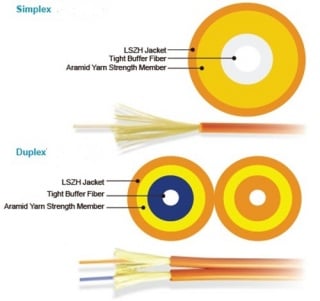
Many types of fiber jumpers have been developed at different times, for different purposes. On the basis of cable quantities, fiber jumpers can be divided into two types, simplex fiber jumper and duplex fiber jumper. The two fiber jumpers are completely distinct from structure to working principle, which can be used for different applications. From the following figure, you can learn that the left fiber jumper is a kind of simplex fiber jumper and the right one belongs to duplex fiber jumper.
Structure Comparison
Simplex fiber jumper is tight-buffered and jacketed that has only one fiber cable with one optical core and cladding. The signal will be transmitted over the one fiber cable. In contrast to simplex fiber jumper, duplex fiber jumper is also tight-buffered and jacketed, but has two separate simplex fiber cables working at the same time. The two separate simplex cables have their own jackets linked together by a kind of material. More detailed information about structural differences for simplex and duplex fiber jumpers is shown in the figure below.
Working Principle Comparison
As for duplex fiber jumper, it works simply, transmitting the signals by two separate simplex cables from opposite sides. When one cable is sending the signal from one side, another cable can receive the signal and send another signal from the opposite side simultaneously. The speed of transmitting signals over duplex fiber jumper is slower than over simplex fiber jumper, while the reliability of transmitting signals by duplex fiber jumper is higher. For the sake of high reliability of sending and receiving signals, the duplex fiber jumper must be highly recommended.
Completely different from duplex fiber jumper, simplex fiber jumper has only one fiber cable, which means the signal transmission through simplex fiber jumper can be only running in one direction at a time. That’s to say, when the signal is transmitted from one side of the fiber jumper, the other side cannot sending another signal until receiving the previous signal. It is really inconvenient and cannot meet the requirement of the market.
As time goes on, a new type of simplex fiber jumper is developed, designed for transmitting the duplex signals respectively over one fiber cable by using two optical signals with different wavelengths. Hence, the data can be transmit in two directions at the same time. In simple words, when one signal is sending from one side of the fiber cable, another signal with a different wavelength can be also sending from the other side at the same time, without mutual interference. Compared to the duplex fiber jumper, the simplex fiber jumper has a great improvement in the high speed of sending and receiving the signals, which also saves the optical fiber resource.
Conclusion
Did you get the detailed differences between simplex fiber jumper and duplex fiber jumper from this paper? If high reliability is required, you are suggested to choose duplex fiber jumper for your network; for the sake of transmission speed, simplex fiber jumper must be a good choice. Besides, except for simplex and duplex fiber jumper, fiber optic patch cord manufacturer has manufactured many other types of fiber jumpers to meet the market needs since fiber jumper has become an indispensable device in today’s optical network. You should master the features and applications of each fiber jumper, so that you can easily choose the right one for your own network.
komentiraj (0) * ispiši * #
Multimode Patch Cable Solution
petak , 21.10.2016.Great Challenge with Existing Multimode Patch Cables
As we know, single mode fiber cables are suitable for 10 Gigabit Ethernet due to its advantages of high speed and capacity. For instance, LC to LC single mode fiber patch cable and LC to SC single mode fiber patch cable, work with high-performance in 10 Gigabit Ethernet. However, taking the manufacturing cost of single-mode patch cable into consideration, it still can’t be largely used in 10 Gigabit Ethernet at present. How to lower the cost without loss of transmission quality? Is there another patch cable with low cost that can substitute for single-mode patch cable, so that it can be deployed in a cost-effective manner in today’s fiber optic market? In order to solve this, researchers attempt to improve the performance of multimode patch cable to support 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
Emergency of OM3 Patch Cable
With the increasing improvement of network, 10 Gigabit Ethernet seems to have been inevitable, which also brings a big challenge to multimode patch cable. Accordingly, enhancing the performance of multimode patch cable has become an inexorable trend.
It is well known that traditional multimode patch cables are used to be applied in 100 Megabit Ethernet and 1 Gigabit Ethernet applications. Is it also able to support 10 Gigabit Ethernet? With the birth of OM3 patch cable, the answer is yes. (The word “OM” stands for optical multimode.) To fulfill the requirement of fiber optical market, the advanced multimode patch cable, OM3 patch cable is developed which can be also applied in 10 Gigabit Ethernet and transmit the signals at lengths up to 300 meters. As for the cost, it is just a little bit more expensive than original multimode patch cable that meets our need. The patch cables in the following figure are the OM3 patch cables, which are largely used in high-speed communication nowadays.
Superior OM4 Patch Cable
Apart from OM3 patch cable, there is a more superior multimode patch cable, OM4 patch cable which has come to fiber optic market. It is designed to support 10 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 550 meters, which also supports 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet at lengths up to 150 meters. With the development of OM4 patch cable, the 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet could be available easily with a cost-effective method, thereby big preference is provided for the users. The patch cable in following figure is a kind of the OM4 patch cable for your reference.
Differences Between OM1, OM2 , OM3 and OM4
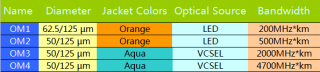
Compared with the OM1 and OM2 patch cables, OM3 and OM4 patch cables have been improved in many aspects. As for the diameter, both of their cladding diameters are 125 µm, but their core diameters are different. In details, the core diameters of OM1 patch cable is 62.5 µm, while the core diameters of OM2, OM3 and OM4 patch cables are smaller, 50 µm. As for the jacket colors, OM1 and OM2 patch cables are orange, but OM3 and OM4 are aqua. As for the optical source, traditional LED is used in OM1 and OM2 patch cables, as VCSEL is used in OM3 and OM4 patch cables with a lower loss. Besides, the bandwidth of the patch cables is designed to be wider and wider to face the high-speed network. From the following figure, we can know exactly the details of four multimode patch cables.
Each multimode patch cable is suitable for different applications. Generally, OM1 patch cable is always used to support 100 Megabit Ethernet applications at lengths up to 2000 meters; while OM2 patch cable is more commonly applied in 1 Gigabit Ethernet within a 550-meters transmission distance. As for OM3 patch cable, it is designed to support the applications of 10 Gigabit Ethernet, and its transmission distance can be 300 meters. As for OM4 patch cable, it is more superior that can support 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet and transmit signals at lengths up to 150 meters.
Conclusion
The development of science and technology will never stop, so does the improvement of multimode patch cable. With the unremittingly increasing requirement of today’s optical network, the multimode fiber optic cables would be developed to support 100 Gigabit Ethernet with longer transmission distance, even support 120 Gigabit Ethernet.
komentiraj (0) * ispiši * #